How To Sell Your Quality Management Plan
Your quality management plan can deliver bottom-line benefits.
SPC DEMO
Don’t miss out! Book a demo of our specialized SPC software and unlock immediate improvements in your processes.
When You Measure the Impact of Quality Management, You Can Make a Powerful Business Argument for Continuous Improvement.
If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it—right? Wrong. When you invest in quality, you lower costs.
Every manufacturer knows that scheduled and preventive maintenance are required to keep operations moving at top capacity. And upgrades are expected to stay ahead of competitive threats, especially when it comes to customer-facing channels and back-office capabilities.
And yet, many quality professionals still use clipboards, pencils, and paper to manage quality on the plant floor. Even top-of-the-line, new equipment is monitored manually.
Plant workers are ready for modern quality management tools, and for more efficient ways to do their jobs. Technology isn’t a barrier for operators. In fact, technology is a natural part of their daily lives—until they get to work. It’s time to equip your workers as modern manufacturing professionals.
With the right quality management tools, plant operators can work more collaboratively with managers, quality professionals, and C-suite executives. Together, they can uncover the greatest opportunities to transform quality—and meet strategic objectives—across the company.
Investments in quality far outweigh the costs of mistakes, inefficiency, and waste. And modern quality management tools build accountability, engagement, and quality into everyday work tasks.
When you give workers the best—and right—tools for the job, the benefits add up fast.
Learn how to quantify the advantages of a strong, technology-driven quality management plan—and build a business case for modernization.
It’s time to modernize. Start building the business case for a technology-driven quality management plan.
How To Get Buy in? Start with Your Stakeholders.
Does change sound painful? Time consuming? Too difficult to justify?
Remember, quality management is a discipline—it means practicing and improving quality management every single day. That requires investing in quality.
Luckily, digital quality management tools can eliminate some of the most challenging aspects of change.
- Poor communication: Modern quality management tools pool all your quality control data into one centralized server—increasing visibility, communication, and collaboration across the company. In contrast, companies using manual processes may rely on face-to-face exchanges or a mishmash of communication methods—email, team meetings, and floor notices—to explain changes, expectations, and results. Quality management tools improve communication, even as you transition to digital solutions. Plus, they keep everyone apprised and aligned as quality needs and initiatives evolve.
- Ineffective documentation: Where are your manual processes stored—in someone’s head? And how do you keep track of process change and revision history? Technology-driven quality management processes are easier to implement, manage, and standardize across your company. Once a process and parameters are set, the system ensures that everyone—at every site—follows them precisely. When it comes to quality control documentation, modern quality management systems store all control metrics, and alert you when collections are missed or incomplete. That way, you know quality management practices are working.
- Insufficient training: Well-planned projects can fall apart if people aren’t properly trained to implement them. In a manual quality world, workers might deviate from the script after training or implement quality practices differently at different sites. Digital quality management technology simplifies training by creating one system—and one way for quality management to be delivered across every process, product, and plant.

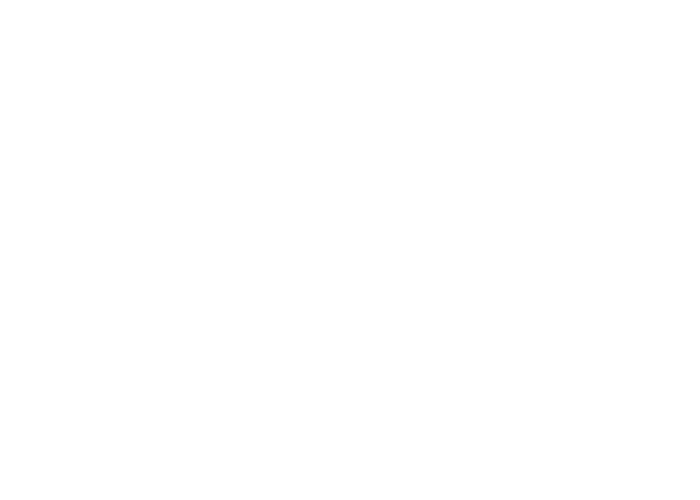
Efficient Data Collection
When quality control data is monitored continuously—in real time—issues get detected and resolved more quickly. At the plant level, digital tools speed up data collection and improve the overall accuracy of the information gathered. With digital data collection, handwritten errors, incomplete information, and inconsistent entries aren’t added to the data set. Digital tools also automate analytics and alerts, ensuring that the right people are notified to act—as issues occur.
At higher levels in the organization, leaders can compare SPC data across shifts, processes, lines, and plants. Reports and dashboards are created automatically, so it’s easier to discover actions that optimize quality. Analysis is more effective and efficient, and best practices can be applied across the organization.
Manufacturing Productivity
Manufacturers want their production lines to run as smoothly as possible and as close to capacity as possible. They use quality control practices to prevent inconsistencies or other failures (such as equipment or raw material defects) that delay operations.
Since most quality managers focus only on their line or shift, productivity gains are limited. But with an enterprise view of quality control data, organizations can compare performance across products, lines, sites, and other variables and arrive at best practices. Then, they can be replicated for greater organizational gains.
Quality & Consistency
Quality control practices help manufacturers meet customer expectations and compliance standards. Quality measures that ensure product consistency, such as net weight and yield, are tracked multiple times a shift. But if those figures sit on a clipboard or get filed away after each shift, they don’t contribute to continuous improvement.
Improving quality and consistency is important for the plant floor—and even better for the enterprise. When quality data is collected digitally and stored in a centralized location, leaders are able to extract more insight and value from the numbers. It’s faster and easier for executives to spot emerging trends and make strategic decisions about quality processes, goals, and investments. With an enterprise view of quality control data, manufacturers can maintain product consistency across lines, shifts, and locations.
Profitability
To improve profitability, manufactures need to reduce scrap, waste, rework, and recalls. But to fix problems, operators have to be able to see problems.
Quality managers use SPC to spot out-of-spec issues that lead to costly mistakes. With elevated, SPC-based quality control practices, you can stop problems before it’s too late to salvage time and materials.
At the line and plant level, quality control improves efficiencies, and can save hundreds or thousands of dollars each shift. Extend those capabilities across the organization, and manufacturers could save millions of dollars. Consolidated, comprehensive, accessible data gives manufacturing leaders more power over the bottom lines.
Reputation & Brand Value
Most manufacturing companies build their brands around quality. But how do they measure it? How do they prove it?
Customer satisfaction, certifications, and successful audits help tell your quality story—when (or because) it’s supported by data.
When SPC data is collected, stored, and reported digitally, it’s easier for manufacturers to validate product quality. In mere minutes, you can verify that checks were completed correctly and on time, and you can respond to customer inquiries—in detail—about specific days, shifts, lines, or lot numbers. Precise tracking helps managers pinpoint root cause, and take immediate action to protect the brand.
These benefits also roll up to the corporate level. Using enterprise-wide information about quality control and performance, leaders can make informed strategic decisions and investments that continuously improve quality—and brand positioning.
Building Benefits for Quality Teams
And what about those gains? Once change has been implemented, everyone starts to experience the benefits of modern manufacturing technology.
Plant-floor Operators
Operators need data and control charts to make decisions (e.g., Do I adjust a machine or not?). But there’s a lot of data to slog through to figure out what matters. It’s time consuming, tedious, and error prone. Operators risk missing an important trend, or jumping in to “fix” things before they need remediation.
Modern quality management tools help plant-floor operators focus on their specific areas—not everything all at once.
• The data they need is automatically calculated—and charted into formats they can use
• Relevant data collections are presented up front to reduce distractions
• Notifications and alerts let operators know when rule violations or other issues need their attention
• Quality issues are automatically documented, graded, and prioritized
Plant Managers & Quality Professionals
Plant managers and quality professionals need data to develop and measure process improvements. But if they rely on manual processes, they may spend more time managing data than managing quality.
Manual data collection is time consuming—and may result in critical analysis gaps. Entries could be missing, inaccurate, or incomplete. And without the ability to efficiently filter and organize information, quality data quickly loses its meaning and value.
Digital quality management tools take away painstaking data management tasks, enabling managers and quality professionals to see the insights in their data faster—and more clearly.
- Data collection, calculation, and reporting are automated
- Data and reports are accessible any time, from anywhere, and can be analyzed in real time or historically
- Because data is complete and consistent, it’s easier to compare quality across processes, equipment, and shifts
- Data can be retrieved quickly to answer audits or customer requests
Corporate & Executive Leaders
Manufacturing leaders need to ensure product quality and consistency across the entire company—not just for a single line or shift. And they need to find high-impact improvements that move the company toward its strategic goals.
If data is managed manually—or differently by site or product—it can be challenging for leaders to enact meaningful change. There’s too much data—with too much variation—for any of it to be actionable. Opportunities are lost in the weeds, issues are difficult to prioritize, and it’s impossible to replicate best practices.
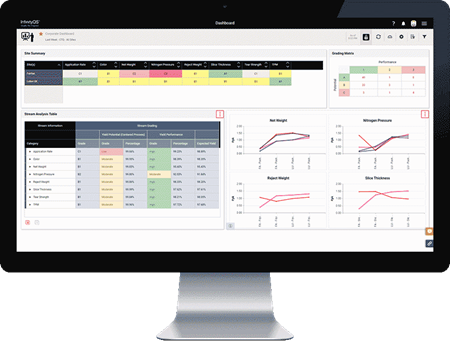
Modern Statistical Process Control (SPC) software centralizes and unifies quality data, giving leaders better “raw material” to build decisions with. Quality intelligence tools also analyze the data automatically—and present it graphically to executives for quick decision making.
- Executives can act with confidence since data feeding their decisions is complete, accurate, and reliable
- Leaders can access all quality data in a unified, central repository—gaining a big picture view, and the ability to drill into line-level performance
- Advanced analytics tools “grade” and prioritize quality issues to help identify quick wins—and biggest risks
- Advanced reporting tools “slice and dice” data, and connect it to actionable strategies
The Costs of Quality
A quality management discipline requires investment—but it’s not a line-item expense. Quality management practices cut across departmental boundaries to improve operations—and lower manufacturing costs—overall.
With a focused quality management plan, you could:
- Reduce overfill and waste
- Increase yield
- Maximize uptime and machine utilization
- Improve operator productivity and performance
- Lower workforce overhead
- Retain and attract new customers
Quality management has a direct link to the bottom line. So how do you start generating ROI from your quality management plan?
With SPC-driven quality management tools and plans:
- Operators work more efficiently when they’re supported by quality intelligence
- The right people get the right information—when and where they need it—to understand and resolve problems
- Data triggers actions on the floor, which eliminates guesswork, biases, and inconsistency
- Performance issues become visible in dashboards and charts, providing managers with visual representations of problems—and their potential impact
- Root cause is easier to investigate using standardized and centralized data
- Opportunities are easier to prioritize with advanced analytics
- Solutions are easier to replicate and standardize across the business
Can you see opportunities for improvement?
You may suspect that your processes are underperforming, but with modern, digital quality management tools you can actually see the difference quality makes.
Easy to start. Easy to expand.
nEnact empowers you to quickly realize the benefits of digital data collection and analysis. Start today with:
- Five Enact licenses: add more as needed
- Quick Setup wizard: your guide to configuring data collections
- Video tutorials and easy-to-use help: available in our Guided Learning Center
- Flexible expansion: reconfigure your licenses, add licenses, integrate with other manufacturing systems, and move to automated data collection—at any time
Implementing Your Quality Management Plan
- Remember: quality management is an ongoing process—not a one-and-done project. The goal is continuous improvement. Start to think about quality management as a phased process versus a final destination.The SPC-based software you need to support your quality management plan can generally be deployed in three stages: proof of concept, pilot, and rollout.
Phase 1: Proof of Concept
Choose a single line or machine to serve as the foundation for your rollout—and a blueprint for your organization.
A focused deployment on a small scale shows operators how to use digital tools to capture data—making tedious manual data collection a thing of the past. Managers and executives will learn how digital analysis and reporting work and can explore the impact.
To plan a successful proof of concept:
- Start small; use a single process (line or machine).
- Document the “before” status so you can demonstrate a measurable impact.
- Prepare master data, such as parts numbers and specification limits. Data may reside in multiple locations, so a proof of concept gives you a jumpstart on centralizing critical quality data.
- Involve multiple experts, including operators, managers, and engineers. Ask them to enter data, interact with it, and provide feedback.
Phase 2: Pilot
During the pilot phase, you’ll apply lessons learned during the proof of concept to expand across the facility. As you add more products and parts to the quality platform, you can include additional functionality—and reporting will become richer. Then you will start to see the significant time savings provided by automated data collection, reporting, and analyses.
During the pilot:
- Pick an expansion path that’s similar to your proof of concept; similar lines or sites will be able to leverage configuration work you’ve already done—and can be spun up faster.
- Focus on standardization to maximize the advantages of a centralized quality system, sync your metrics, analyses, naming conventions, and work practices.
- Dig deeper. Now that you have more data feeding into the repository, it’s time to explore advanced features and capabilities.
- Create documentation to prepare the rest of the organization, such as training materials. You can also start to estimate the resource requirements needed to support a complete rollout (e.g., time and staffing).
Phase 3: Production Rollout
Lather, rinse, and repeat! After a successful proof of concept and pilot, it’s time to apply your blueprint to other parts of the company. You can expand your modernized quality management process to other lines, facilities, and processes—and throughout the organization. As you continue developing your quality management approach, data and value will grow.
With accurate, consistent, and complete data from across your manufacturing organization, the business case for quality becomes stronger and stronger. Once fully deployed, you can:
- See the biggest opportunities for process and product quality improvement
- Prioritize opportunities—and designate the resources needed to address them
- Develop policies and processes that affect bottom-line performance
- Use quality improvement to address strategic priorities
- Empower workers—and create a culture around quality

“At the beginning of our proof of concept, the plant manager wasn’t into it. By the end, he was in love with it—and is now Enact’s biggest advocate. We’re actually using the system to effectively communicate between quality and production.”
— Jegadish Gunasagaran, QA Associate
Bakery on Main
Speak to a Distribution Industry Expert
What to Expect
- Free 20-minute call with a product expert
- Explore which solutions best suit your needs
- No-pressure conversation
- Get a live, personalized demo







